- Children’s Museum
- NMK Magazine
- Museum Shop
- Related Site
- Gyeongju National Museum
- Gwangju National Museum
- Jeonju National Museum
- Daegu National Museum
- Buyeo National Museum
- Gongju National Museum
- Jinju National Museum
- Cheongju National Museum
- Gimhae National Museum
- Jeju National Museum
- Chuncheon National Museum
- Naju National Museum
- Iksan National Museum
- Cultural Foundation of National Museum of Korea
- Friends of National Museum of Korea
- The Korean Museum Association
- Language
Prehistory and Ancient History
The Prehistory and Ancient History section displays artifacts that represent some of the earliest evidence of Korean civilization and culture, from stone tools of the Paleolithic age to gold jewelry of the Silla Kingdom and stone monoliths of the Balhae era, with each room documenting those aspects that uniquely define each of Korea's different periods of ancient history.
-
Neolithic Period
-
Location
Showroom
Introduction
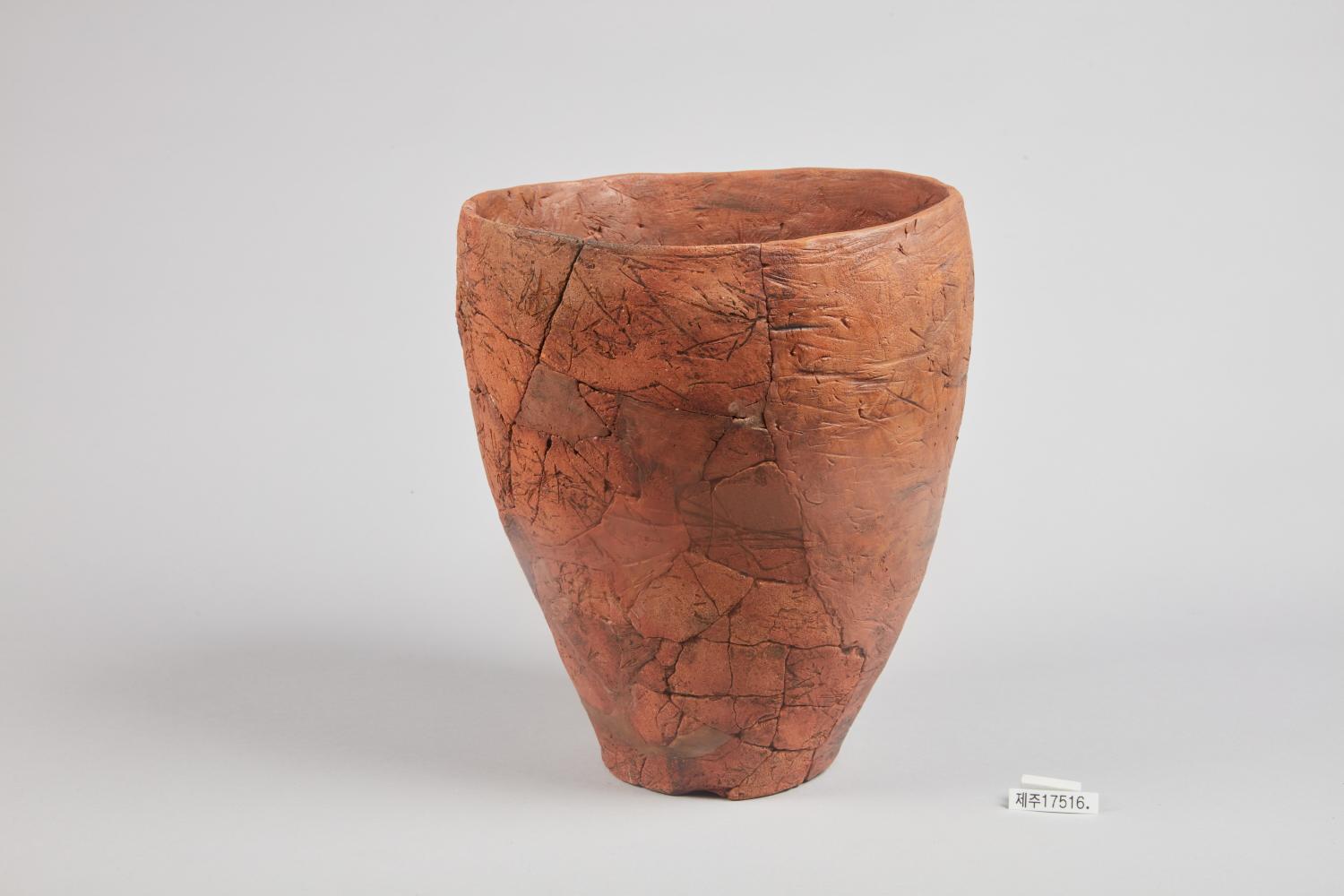
- The Neolithic Period, in Search of a New Way of Life
- The Neolithic Period on the Korean Peninsula spans from about 8,000 BCE to 1,500 BCE. The last ice age ended around 10,000 BCE when temperatures began to increase. By around 4,000 BC, the coastline achieved its present-day form.
- Neolithic communities had to find new ways to survive in the warmer environment. Larger animals had disappeared along with the glaciers, and so they used bows and arrows to hunt smaller, faster animals instead. They lived in semi-subterranean houses, picked berries, and began to practice small-scale farming. They also fished in the seas and rivers.
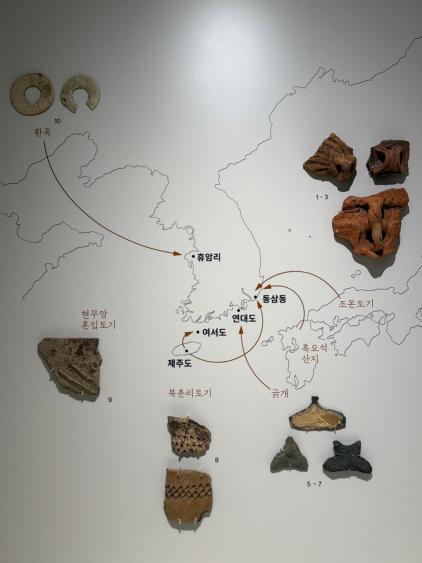
- Neolithic people made tools from stone and bone and produced the earliest pottery. The pottery vessels were used to store and cook food. They traded with people across the seas for objects that they needed.
-
-
-
Location
-





 X
X  Facebook
Facebook